Indonesia is urbanizing fast. In 2010, just over half of the country’s population lived in cities. As of 2023, that figure has jumped to 58.57% or about 164.7 million people. By 2024, the number is expected to reach 165.7 million, with an annual growth rate of 2.05%. This pace of urban growth presents both major challenges and real opportunities. On the surface, more people in cities means a larger workforce, more innovation, and better access to services. But Indonesia urbanization trends also expose weaknesses in infrastructure, housing, and basic service delivery.
Urban Growth Outpacing Infrastructure
Urban areas are Indonesia’s economic engine. Between 2010 and 2016, cities generated nearly 60% of the country’s GDP, and Jakarta alone produced almost 25%. Yet the economic benefits are uneven. For every 1% increase in the urban population, Indonesia’s GDP per capita rose by only 4%. That’s far behind China (10%) and Vietnam (8%), suggesting untapped potential.
Part of the reason is poor infrastructure. The government needs to invest $60 billion each year just to keep pace with urban growth. That includes roads, energy, water, and public transit. But right now, only 48% of urban households have access to piped water. Many city dwellers also face traffic jams, limited sanitation, and unreliable electricity.
Read Also: Advancements in Indonesia Urban Transit Projects & Systems
The Rise of Satellite Cities and Urban Sprawl
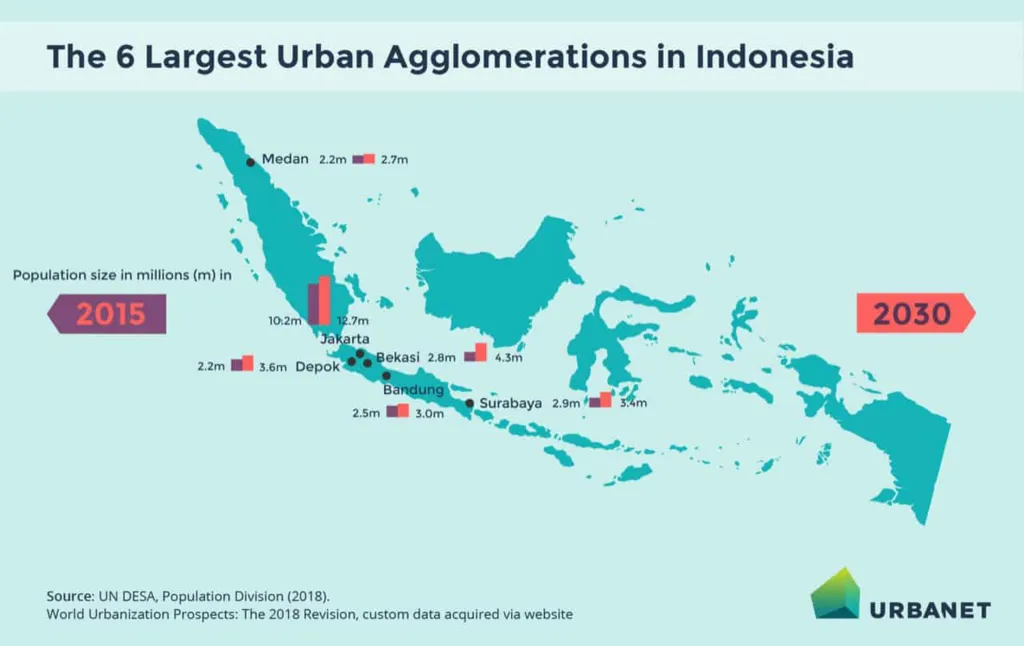
As Indonesia’s major cities like Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bandung become increasingly congested, a new trend is emerging: the growth of satellite cities and peri-urban areas. The government’s National Strategic Projects (PSN) program aims to develop 10 new urban centers outside Java, including:
- IKN Nusantara (the new capital in East Kalimantan)
- Pekalongan Metropolitan Area (Central Java)
- Mebidangro Urban Agglomeration (Medan-Binjai-Deli Serdang-Karo in North Sumatra)
Indonesia Urbanization Trends: A Housing Crisis Unfolding
Housing is another urgent issue. Indonesia is facing a deficit of 13 million housing units by 2025. The problem isn’t just quantity but affordability. Over 30 million Indonesians live below the poverty line, and many live in cramped, informal settlements without secure tenure.
Read Also: The Struggle of Indonesia Affordable Housing Challenges
As cities expand outward, they consume farmland and natural ecosystems. That adds to environmental pressure and increases the risk of floods, especially in low-lying areas prone to land subsidence and climate change impacts.
Changing Cities, Changing Lives
Urbanization is changing how people live, work, and move. While ATMs and branch banks shrink in relevance, demand rises for smart infrastructure, digital public services, and sustainable housing models. The shift is rapid, but the supporting systems often lag.
The good news is that this challenge brings opportunity. If the government can close the infrastructure gap, expand affordable housing, and improve service delivery, urban growth can lift incomes, improve productivity, and boost quality of life.
Indonesia Urbanization Trends: Turning Urban Growth Into a Win
Indonesia urbanization trends highlight a critical crossroads. On one side: fast growth, vibrant cities, and rising economic potential. On the other: strained infrastructure, housing shortages, and gaps in basic services. The path forward is not easy, but it is clear. With bold investment, smart planning, and inclusive urban policies, Indonesia can turn its urban boom into a long-term advantage. The next decade will be crucial in deciding whether its cities become engines of prosperity or centers of inequality.






